Top 07 Reasons to use Laser Scanning for Construction Projects in 2026
By 2026, the global construction market will enter a significant paradigm shift, characterised by precision, data-driven processes, digital twins,...
9 min read
![]() Brighter Graphics
:
Oct 25, 2025 11:10:14 PM
Brighter Graphics
:
Oct 25, 2025 11:10:14 PM

The gap between design accuracy and on-site execution can determine whether a construction project succeeds or fails. Even with advanced digital modeling and detailed planning, the gap between concept and reality remains a significant challenge, manifesting in budget overruns, schedule delays, and safety risks. Sometimes, even a few centimeters off can lead to costly rework, compliance issues, and operational inefficiencies.
That’s where construction verification steps in. It bridges the gap between design and reality by using laser scanning, Building Information Modeling (BIM), and reality capture to confirm that what’s built matches the approved plans.
While BIM tools are becoming ever more common, adoption remains slow, and their real-world impact remains limited. According to McKinsey, the global construction industry generated about $13 trillion in 2023 and is expected to hit $22 trillion by 2040, yet productivity growth between 2000 and 2022 averaged just 0.4% per year. This slow progress shows why construction verification is so necessary, not just for compliance but also as a key driver of absolute efficiency, accuracy, and measurable improvement across projects.
Let’s unwrap the key concept of construction verification before exploring it further.
Construction verification is a computer-based quality assurance process that verifies that the physical construction aligns with its design requirements and standards. It provides an objective comparison of the “as-designed” model and the “as-built” condition using 3D spatial data.
BIM (Building Information Modeling) serves as the backbone of this process, acting as a central hub for coordination, validation, and communication. When combined with construction verification, it helps teams build with greater precision, confidence, and efficiency.
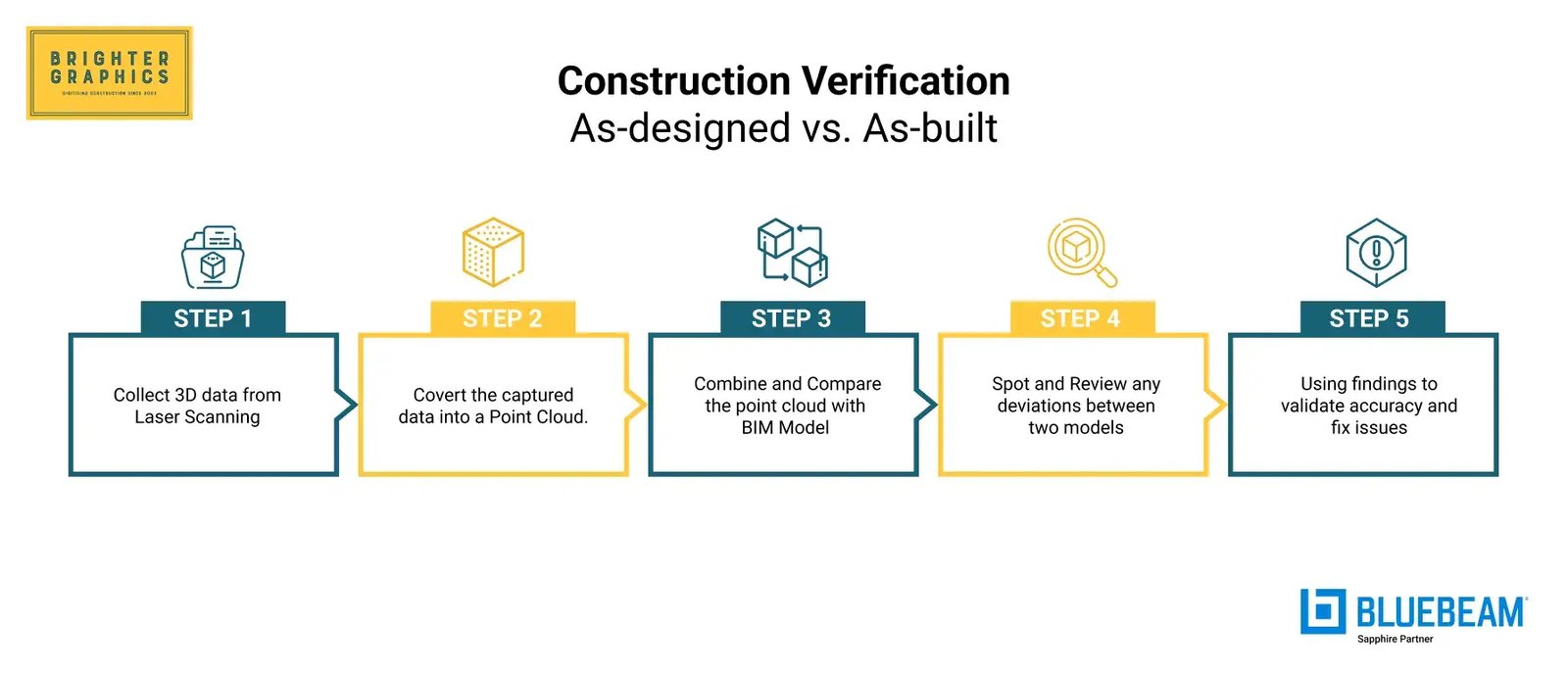
The process typically goes like this:
Step 1: Collecting detailed 3D data from the construction site using laser scanning or reality capture.
Step 2: Converting the captured data into a three-dimensional representation (point cloud) of the physical environment.
Step 3: Combining the point cloud with the Building Information Model (BIM) to compare the as-built structure with the as-designed version.
Step 4: Spotting and reviewing any deviations or differences between the two models to see where things don’t line up.
Step 5: Using these insights, design and construction teams can validate accuracy, fix issues early, and prevent costly rework.
Verification isn’t just about checking for accuracy; it directly impacts cost control, risk management, and compliance. When builds go unverified, minor errors can quickly snowball into major problems.
Rework alone is one of the biggest culprits behind budget overruns and schedule delays. According to recent studies, the direct cost of rework in construction projects can range from 2.4% to 12.4% of the total contract value, often caused by misalignment between design intent and what’s actually built on-site.
By incorporating construction verification, teams can spot deviations early, reduce risks, and maintain consistent quality throughout the project. On top of that, digital verification helps ensure compliance with safety regulations and building standards, especially in complex projects such as high-rise developments and public infrastructure.
Back in the day, verification mostly meant manual checks, tape measures, and drawing over 2D plans. That worked fine for simpler builds, but as projects grew more complex, those methods began to fall short due to human error, inconsistencies, and limited precision.
However, the shift to digital verification changed the game. Now, technologies such as 3D laser scanning, mobile mapping systems, and spatial data analysis enable millimeter-level precision. Many high-quality 3D scanners achieve accuracy within tenths of a millimeter. Some structured-light scanners even report global uncertainty around 0.05 mm in ideal conditions. This level of detail lets you build a virtual twin of the site, so you can directly compare what was designed vs. what’s being built.
Digital verification turns quality assurance into a proactive tool rather than a “check at the end” step. With automated alignment, deviation analysis, and integrated reporting, you can catch issues early and keep your construction running smoothly.
The core of the construction verification is 3D laser scanning, the methodology that registers millions of data points per second to generate a high-definition digital duplicate of the construction world. It is a physical-to-digital reality-capture process that produces data points for the accurate foundation of 3D models.
With 360-degree imagery and point cloud data, project teams can visually inspect, measure, and validate all components without relying on manual measurements. The cloud data is used to create precise 3D models.
Laser scanning, in combination with BIM verification, ensures that quality assurance (QA) and quality control (QC) are not intermittent but rather data-driven, ongoing practices integrated into day-to-day activities.
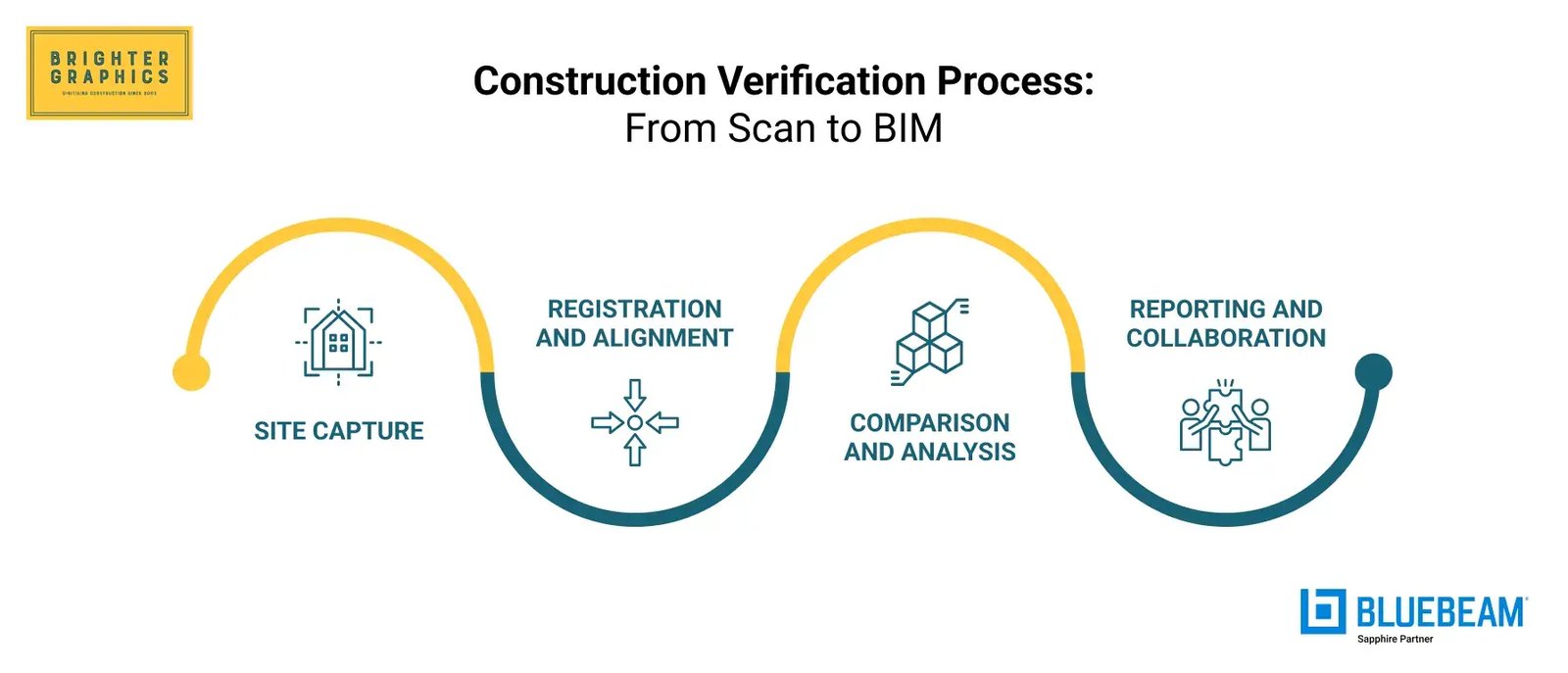
The verification workflow typically follows a structured sequence:
This process helps keep the current construction progress under constant monitoring, confirm work completion, and ensure team compliance. For an in-depth technical breakdown of the entire process, read our Scan-to-BIM blog.
The accuracy and speed of the check are improved with automation. BIM-embodied verification software can autonomously identify areas with out-of-tolerance conditions, generate deviation heat maps, and issue corrective action warnings.
Besides eliminating subjectivity in the manual process, these digital QA tests also enable remote tracking of the project. Real-time assessment of shared data can be conducted by teams in various locations, enhancing coordination and decision-making.
In addition to accuracy, construction verification results in quantifiable benefits in time, cost, and cooperation:
Verification establishes a verifiable, data-supported source of truth for all stakeholders. Having objective measurements rather than subjective interpretations provides strong confidence in project data. Design deviations and mistakes are detected at the initial stages, thereby avoiding downstream effects.
Cloud-based checking systems facilitate seamless collaboration among architects, engineers, and contractors. The verification data incorporated into BIM models enables all team members to access current project images and track project progress. Such transparency facilitates real-time communication, minimising the chances of ambiguity and ensuring that every party operates on a shared version of the truth.
Checking also reduces material waste and eliminates repetition by verifying accuracy before advancing to the next stage. Early identification of discrepancies minimises the risk of structural clashes, saving vast sums of money and avoiding delays. Additionally, digital verification promotes sustainable construction and effective planning, resulting in reduced waste and a decrease in carbon footprint, as well as improved resource utilisation.
Quality Management Plan (QMP) is the core of all successful projects, and verification enhances it by incorporating digital checks into the construction life cycle.
Testing is a natural fit to prevailing QA/QC procedures. The point cloud information and deviation reports will be considered as digital records of adherence to design requirements and regulatory provisions. Constant monitoring leads to transparency and makes the safety audit easier to complete, as there are no mismatches that are overlooked.
Centralisation of as-built information leads to accountability and traceability during project phases by promoting transparency and accountability. Information from past cycles of the verification process offers significant insight into future design, maintenance, and renovation projects.
The fact that it can link on-site action with office-based project management implies that decisions are made on verified, trustworthy information.
The Building Safety Act 2022 in the UK transformed the country's construction and safety culture. It is also unique in that it introduces a new definition of accountability, transparency, and data integrity during the building lifecycle, and was introduced in the aftermath of the Grenfell Tower disaster.
The Act is more applicable to high-rise buildings (18 meters or seven stories and more), but its influence has now spread to the majority of large-scale projects nationwide.
One of the significant characteristics of the Act is the establishment of Gateway 3, the last compliance inspection point before a building is legally occupied. At this point, developers are legally required to give verifiable materials that construction complies with approved designs, materials, and safety standards. This condition renders digital verification not only a best practice but also a regulatory requirement.

Gateway 3 requires construction teams to provide validated, digital as-built records to obtain approval to occupy. This will contain certified evidence of fire security measures, construction, and system installations. Independent verification ensures the integrity of this information, a component of the Golden Thread of building data mandated by law.
With construction verification as part of this process, project teams can create accurate, time-stamped, and traceable reports of all stages. Laser scanning integrated with BIM verification provides the digital evidence required for certification, significantly reducing the likelihood of non-compliance.
The Golden Thread represents the uninterrupted flow of accurate, accessible digital information throughout the building's life cycle —from initial design to ongoing operation. Construction verification is a direct contributor to this framework due to its capacity to maintain the credibility of as-built information and make it transparent.
For example, verified point clouds and BIM models can be considered a living document of a building's actual state. This traceable information enhances accountability, supports safety audits, and enables informed decisions on maintenance and refurbishment.
Finally, construction verification helps companies fulfill the Golden Thread requirement, ensuring that all information about the building is consistent, validated, and safely stored. This digital continuity instills trust among clients, regulators, and end users and enhances a culture of safety and responsibility within the construction ecosystem.
Construction checking is not only a compliance tool but also a highly effective means of tracking progress in real time and controlling the project. Combining reality capture with Building Information Modeling (BIM) enables teams to verify what has been constructed against the original design continually.
This enables making decisions based on data, improves accountability, and ensures every step of construction is completed on time and within tolerance.
Reality capture enables comparisons made on the timeline, providing a clear view of project development. BIM models can be integrated with progress updates, allowing for the immediate detection of delays or deviations. Virtual walkthroughs created from scan data save time and are safer, as they enable visits to the location to be avoided.
Internet-based systems enable multiple users to access real-time project information. Real-time updates enable stakeholders and clients to view and confirm milestones, using verified information to streamline scheduling and coordination across dispersed teams.
According to LYCA Surveying Data (2025 Dubai Construction Insights), more than 70 percent of all new projects surveyed used drone or 3D laser scanning in addition to conventional survey methods.
Authenticated as-built data is used to create a digital twin, improving management, maintenance, and retrofit of facilities. These models provide reliable and accurate information for the sustainability and optimisation of energy throughout the building's life cycle.
According to a 2025 peer-reviewed study, 52% of the overall project cost increase is attributed to rework, resulting in schedule overruns of up to 22%. Moreover, rework accounted for 7.1 percent of total work time. Also, an annual survey on how Poor Digital Skills Hold Back Adoption of BIM, which surveys almost 300 construction professionals, finds that more than half report using BIM on projects hardly ever, with regular usage among only a quarter of that group.
Although verification technology is highly sophisticated, achieving a good result requires careful planning, technical expertise, and attention to detail. The implementation will require proper data collection, model alignment, and smooth coordination between the site and online teams to be successful.
Brighter Graphics Digital engineering is the pioneer of this change. The company has combined expertise in laser scanning, 3D modeling, and BIM verification to deliver end-to-end digital engineering solutions that ensure accuracy, compliance, and efficiency in construction.
At Brighter Graphics, we use state-of-the-art Trimble X9 scanners and precise reality-capture processes to offer a complete range of scan-to-BIM, as-built verification, and construction progress-tracking solutions. Our methodologies connect both the physical and digital worlds, allowing architects, engineers, and contractors to support design cohesiveness across all levels from Scan-to-BIM-to-Deliver.
This is what you can expect with our Digital Engineering services:
With 30 years of experience serving the Architecture, Engineering, Construction, and Operations (AECO) industry and as a well-established Bluebeam Sapphire partner, Brighter Graphics possesses the capability and flexibility to meet today's digital construction requirements.
Their verification services enable their clients in the UK and Europe to attain unprecedented accuracy, cost management, and regulatory compliance. Regardless of the scale of your project or infrastructure, our team is skilled at delivering confidence through data verification and excellence-focused processes.
Construction verification is a paradigm shift within the provision and management of the built environment. Filling the gap between design and reality, it enables project teams to achieve high levels of accuracy, regulatory adherence, and efficiency across all construction phases.
Amid a highly regulated construction industry and initiatives such as the Building Safety Act, digital verification is no longer a nice-to-have but a must-have. It ensures that all components, including structural factors and fire safety measures, are documented, verified, and up to date prior to occupancy.
In addition, verification is associated with larger objectives of QA/QC excellence, cost assurance, and continuity. With the use of data-driven decisions and ongoing documentation, the industry is moving toward the future, where success is characterised by trust, accountability, and precision.
The Digital Engineering team at Brighter Graphics is the first point of contact for those who are willing to accept validated reality. We have highly developed technologies and a professional staff that ensures all projects, regardless of magnitude and complexity, meet the highest quality standards and are applicable and compliant.
Get in touch with us and take a swift move towards digitising construction to elevate commitment, integrity, transparency, and confidence in building. The future of digitising construction is not only designed, it is confirmed!
By 2026, the global construction market will enter a significant paradigm shift, characterised by precision, data-driven processes, digital twins,...
The new Bluebeam Revu update, version 21.8, is now available. The latest version focuses on simplifying workflows, improving collaboration, and...
When it comes to construction, “close enough” just doesn’t cut it anymore. Owners expect consistent schedules, contractors want zero rework, and VDC...